Medical 3D Printing: Stratasys Technologies, Materials, & Applications
Stratasys is well known for its impressive lineup of professional-grade 3D printers. And, as the demand for 3D printed medical parts increases, Stratasys continues to deliver unmatched solutions to meet these needs.

The development of advanced medical materials has filled a long-awaited void for many healthcare applications. While 3D printers exist that can print a variety of materials with tight tolerances, many medical applications require specific material characteristics to replicate human bone and tissue and/or be sterilizable to meet strict regulations.
Stratasys Medical 3D Printers
Stratasys medical-grade 3D printers and sophisticated materials provide solutions for surgeons, to expedite innovation, improve clinical outcomes, and help advance medical manufacturing.
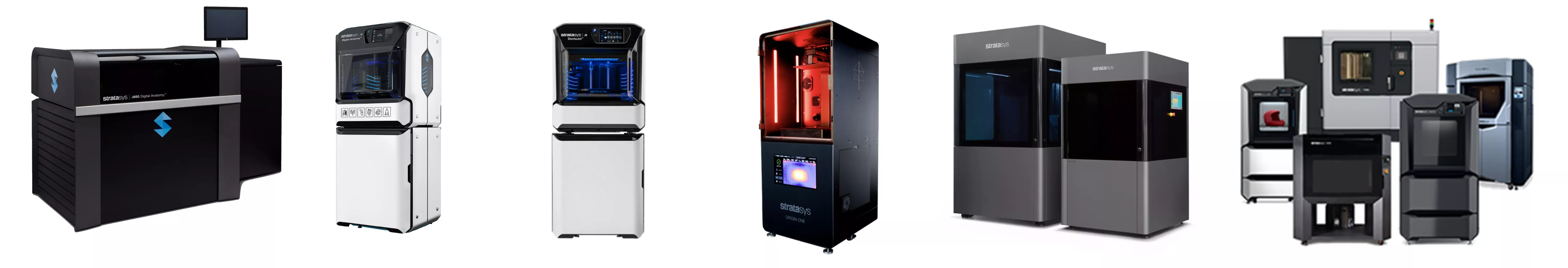

From left to right: J850 Digital Anatomy (DAP), J5 Digital Anatomy (DAP), J5 MediJet, Origin One (DLP), Neo (Stereolithography), FDM Series
J850 Digital Anatomy Printer (DAP)
The J850 Digital Anatomy PolyJet 3D printer creates life-like complex medical models of the highest standards.
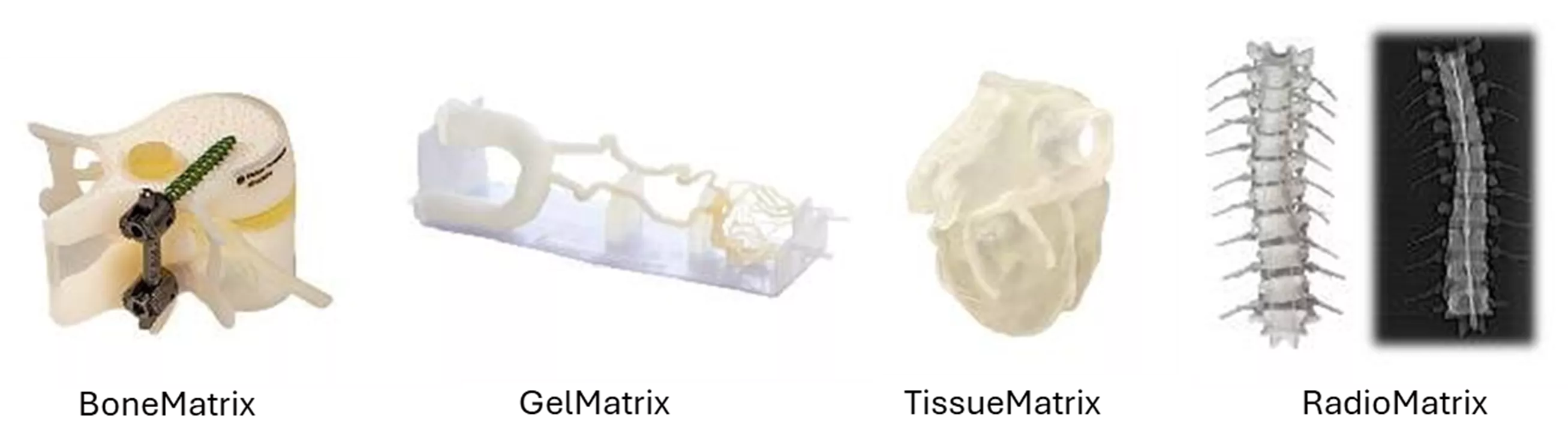
With materials such as BoneMatrix, GelMatrix, TissueMatrix, and RadioMatrix, the DAP material family provides anatomical realism to mimic human bone and tissue characteristics of softness, flexibility, and density. Surgeons around the world use this technology for pre-surgical practice in complex cases as well as educational tools.

J5 MediJet
The J5 MediJet is the premier choice for medical modeling, providing unprecedented capabilities to academic medical centers, hospitals, and medical device manufacturers. With simultaneous access to 5 materials, it's possible to produce sterilizable end-use drill and cutting guides at the same time as stunning multicolor medical models.

Origin One (DLP)
The Origin One is unlike any other resin-based desktop DLP machine. The reliability and repeatability of high-quality production parts allow medical parts manufacturers to produce end-use parts with comparable accuracy and quality to injection molded parts. From functional prototypes to mass production, the Origin One enables the use of a wide range of high-performance materials while holding incredibly precise tolerances needed in the healthcare industry.
LOCTITE ® 3D MED412 and MED413 are both biocompatible to ISO 10993-5/-10 (cytotoxicity, irritation, sensitization) and are often used to create reusable medical components, orthotics, respirator components, lab equipment, skin contact applications, and more.
FDM Series
Stratasys has a wide range of FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) 3D printers that can build parts of all shapes and sizes for a variety of applications, including medical devices. FDM materials ABS-M30i is biocompatible (ISO 10993) and can be gamma or EtO sterilized. ULTEM 1010 has a biocompatibility certification and can be used to create medical tools like surgical guides.
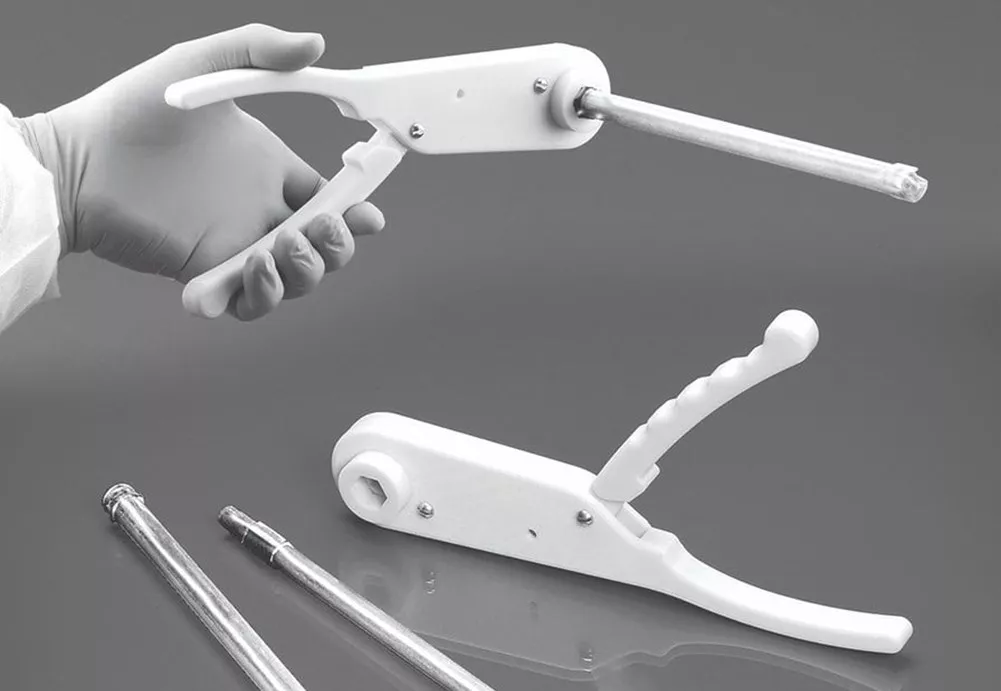
Biocompatible FDM materials are a very feasible way to communicate complex surgical planning techniques and validate new medical device, tool, and fixture designs.
Neo SERIES (Stereolithography)
The Neo Stereolithography 3D printer has proven its reliability in building high-quality parts with superior detail, accuracy, and surface finish. Stereolithography materials have progressed from general-purpose prototyping into high-performance materials that broaden applications into end-use production parts.
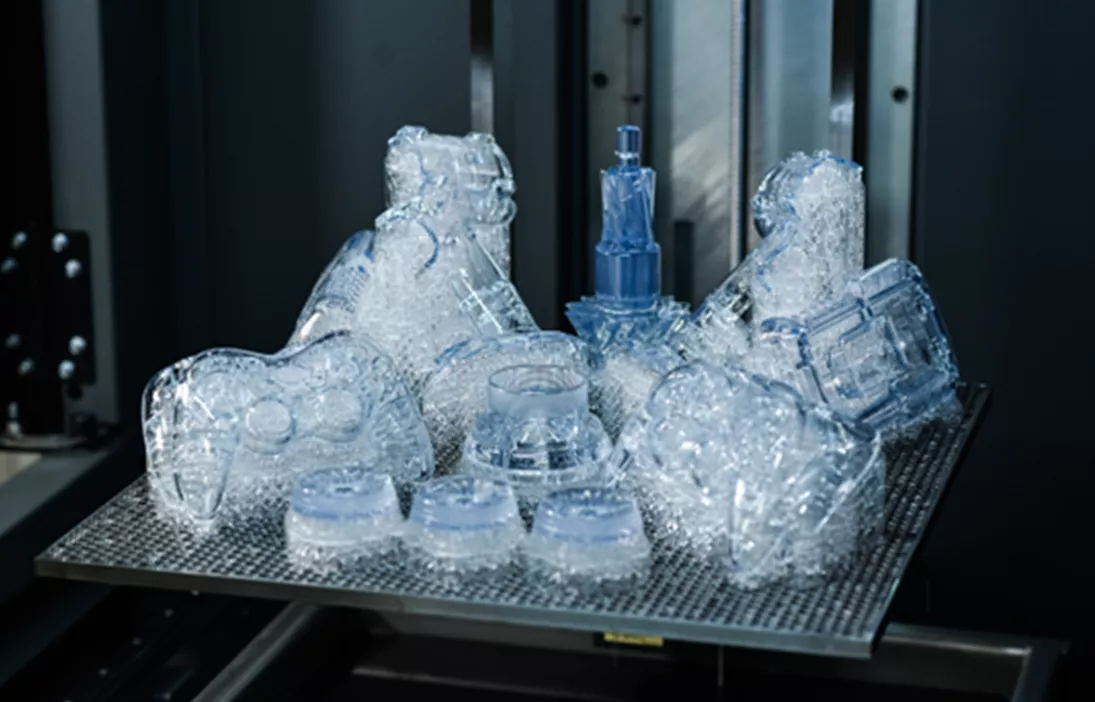

SL materials such as Somos® BioClear, Somos® DXM SL 100, Somos® NeXt™, and Somos® ProtoGen™ 18420 allow for medical applications such as anatomical models, surgical guides, precision-molded internals for prosthetics, and functional prototypes with body contact.
J5 Digital Anatomy (DAP)
Stratasys has recently introduced the J5 DAP to their medical 3D printer lineup. This PolyJet 3D printer is designed to drive innovation in the development of new medical products and procedures. It is used to train surgeons outside the operating room, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced surgery costs. With its low cost of ownership and reduced initial investment, the J5 DAP aims to minimize the need for outsourcing.
If you are interested in learning more about Stratasys medical-grade 3D printers and applications, contact us.
75% Reduction in Prototyping Costs ⋅ 50% Acceleration in Development time
Download this guide to learn how the medical industry is using 3D printing technology to acceleate time to market, optimize product design, elevate cost efficiencies, and reduce development risk.

Editor's Note: This article was originally published in June 2024 and has been updated for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Related Articles
3D Printing in Healthcare: Redefining Surgical Outcomes
Ultimate Guide to PolyJet: Applications, Advantages, History, & More
Experts in Additive: 3D Printing with GoEngineer
Medical 3D Printing: Advanced End-to-End Solutions for Surgeons

About Ryck Hoopes
Ryck Hoopes is a Hardware Application Engineer at GoEngineer. With a background in domestic and international manufacturing, he brings extensive knowledge of R&D, quality control, and supply chain management. Having worked in Aerospace, Healthcare, Marine, and Consumer Goods industries, Ryck is well versed in common challenges many companies face today. When he’s not working, Ryck enjoys mountain biking, snowboarding, and spending time with his friends and family in the mountains. He also coaches little league football, baseball, and snowboarding.
Get our wide array of technical resources delivered right to your inbox.
Unsubscribe at any time.

