Onulis Wrap W7500
Convert 3D Printed UV waste and unused resin into fully-cured, disposable stock
 Now Serving US & Canada
Now Serving US & Canada

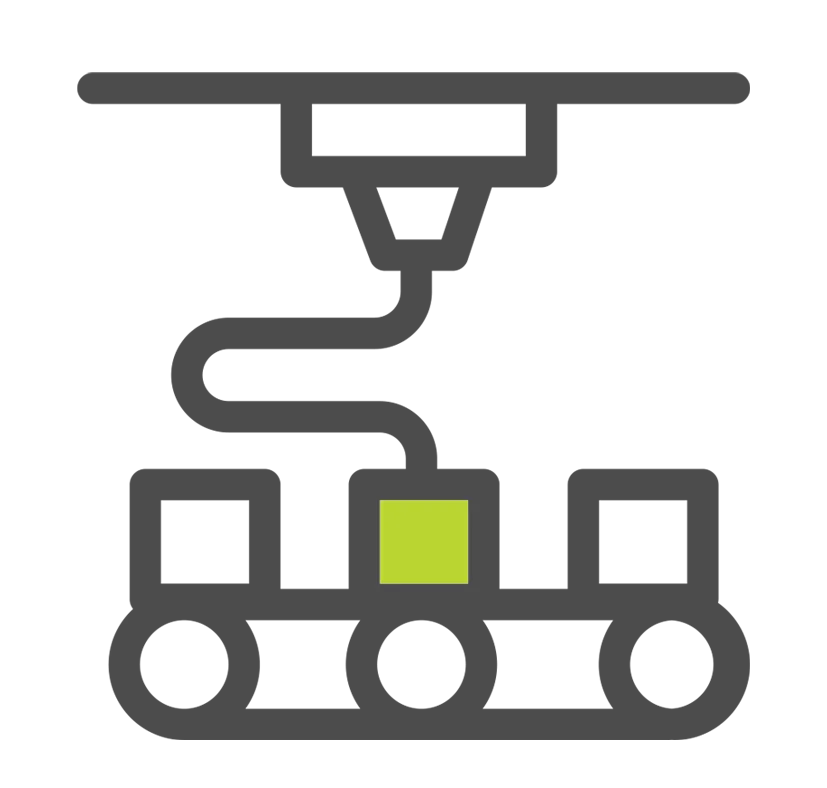
Onulis Waste Resin Axial 3D Printing
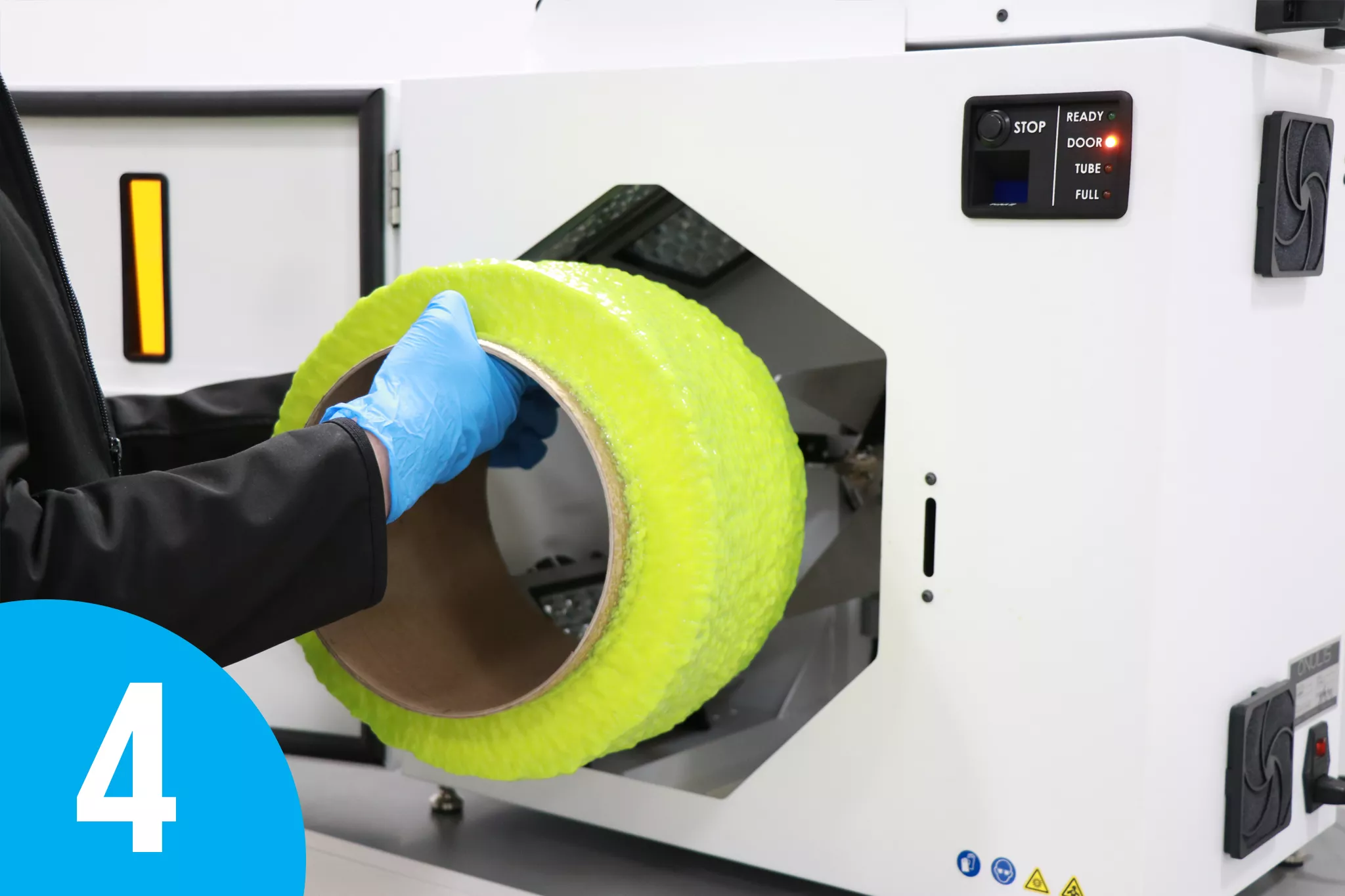
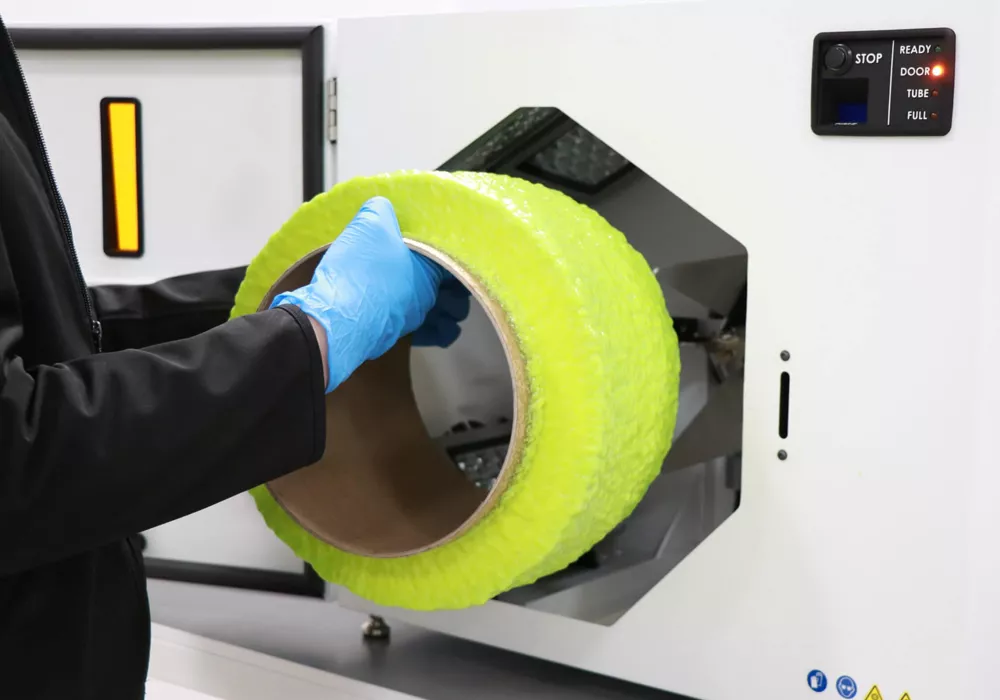
The WRAP W7500 printer creates solid plastic stock for a wide variety of uses, including low-cost media for prototype machining, raw material to produce colorful products, or unique organic shapes to create artwork projects. Leveraging the patent-pending WRAP™ (Waste Resin Axial Printing) technology, which prints with previously used or expired UV resin, the W7500 operates at virtually zero cost. Once your waste resin is printed, it can also be disposed of as standard household waste.
Safely Dispose of 3D Printed Waste
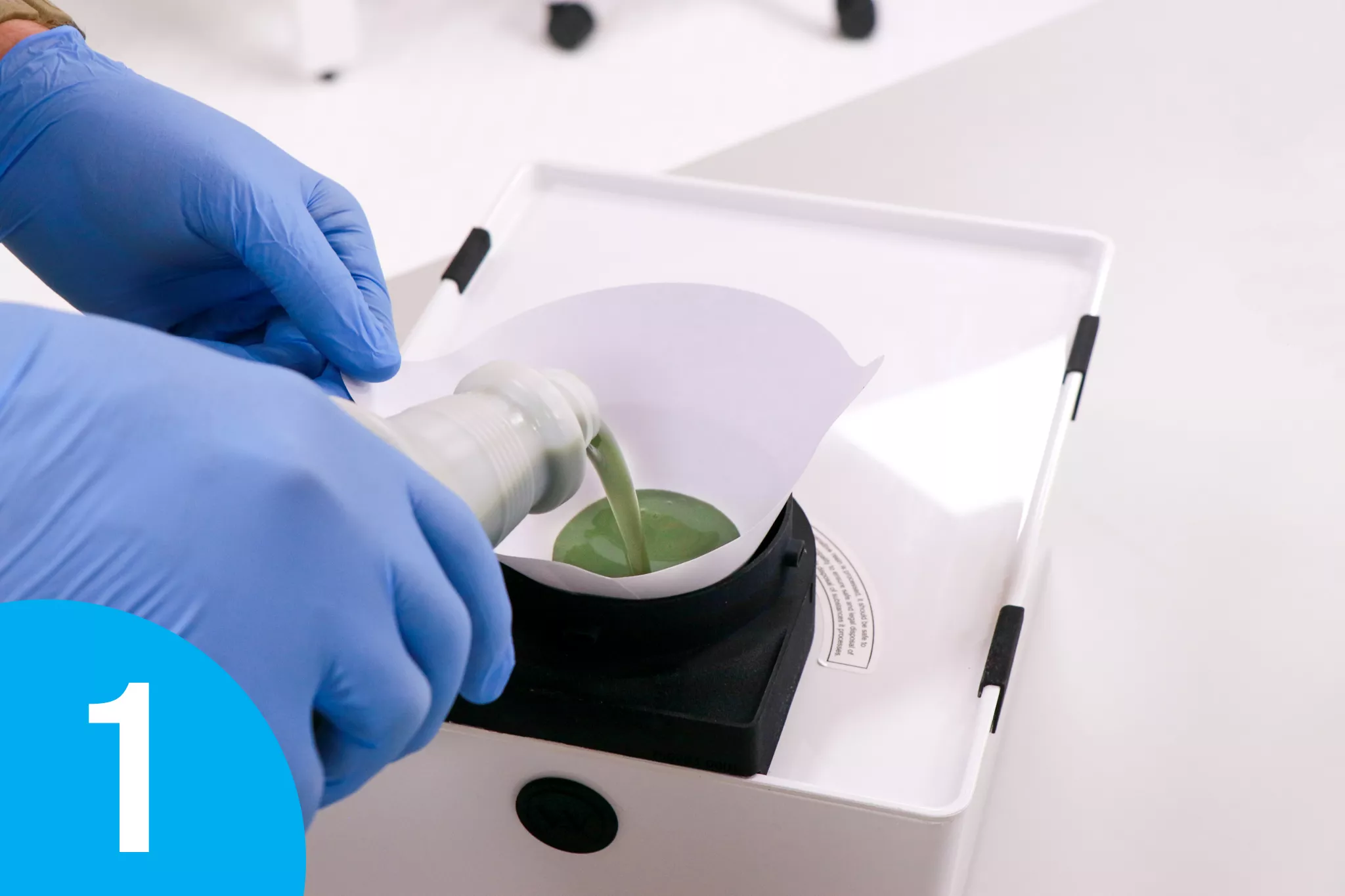
UV resins are typically delivered in a liquid format. Standard disposal of the waste resin generated in the 3D printed process and expired resin is considered hazardous waste and will incur different costs in different municipalities. The WRAP W7500 can eliminate these additional costs. Once the material is printed on the tube, you can safely dispose of it in your standard waste.

Features

-
Automatic timing function and integrated safety features enable unattended operation.
-
W7500’s axial 3D printing architecture minimizes overall size and cost.
-
Through leveraging used or expired resin, operation costs are virtually zero.
-
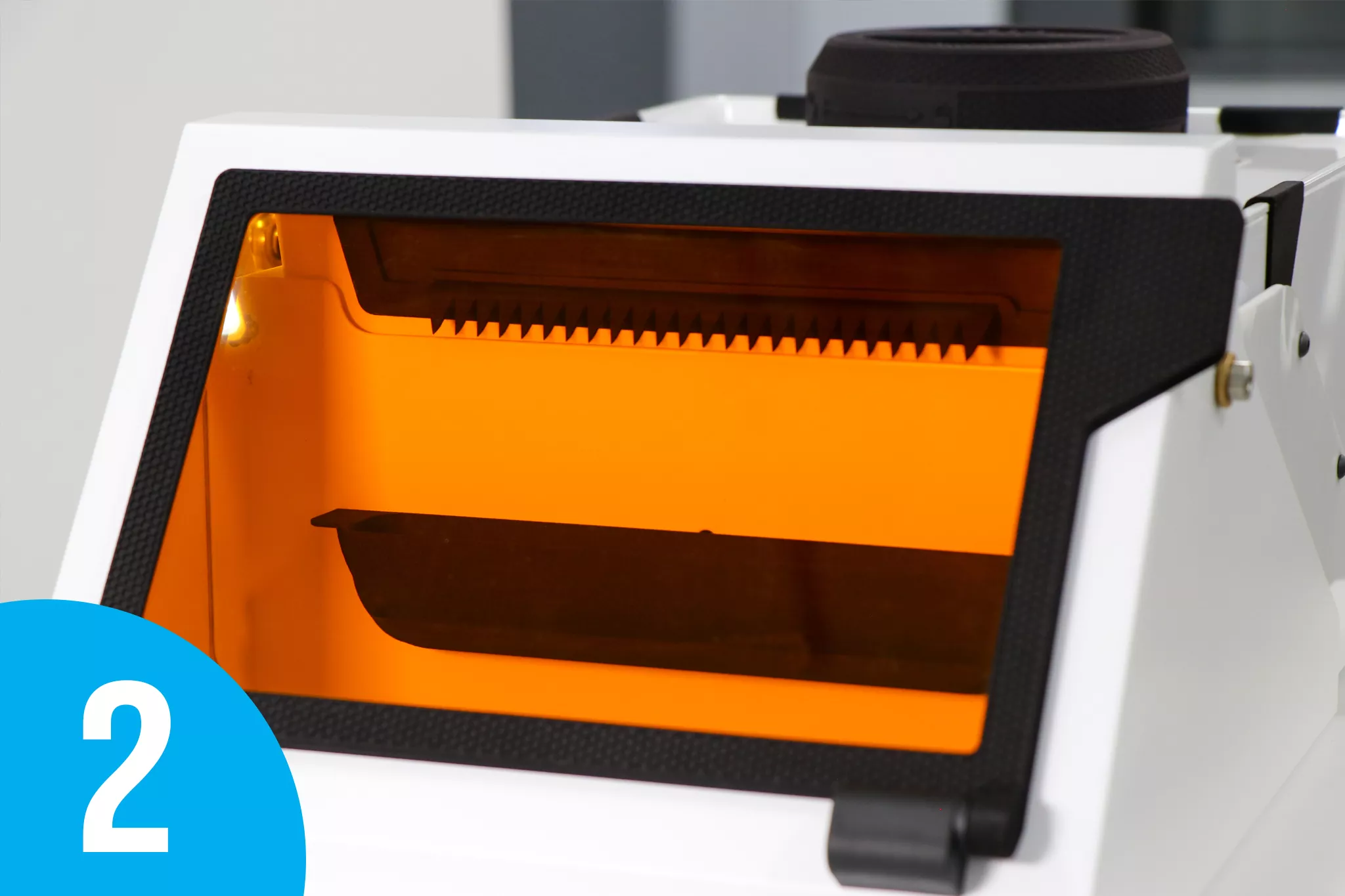
Patent pending drip comb produces individual droplets for efficient curing.
-
Simple gravity-driven drip system avoids use of pumps, valves, and hoses, which are susceptible to clogs.
-
Onboard carbon filtration system controls fumes.
Specifications
Compatible Resins
- Stereolithography
- DLP
- PolyJet
Vat Capacity
7.5 L
Throughput
Cures 30 days’ worth of waste resin in 6 hours
Printed Plastic Stock
14 in. dia. x 8 in. dp. cylinder
System Size & Weight
Standard: 26.5 x 16.5 x 28.7 in.
Extended: 26.5 x 16.5 x 39.2 in.
Weight: 60 lbs
Operating Conditions
Temperature 65 – 95°F (18 – 35°C)
Power Requirements
100 – 120 VAC, 50 – 60 Hz, 6A, 1 phase (switchable to 220)
Consumables
Disposable Tubes (8 pack)
PM Kit, includes:
- Disposable Tubes (8 pack)
- Carbon Exhaust Filters
- Vat with Dispensing Comb
Options
Storage Stand: 28 x 17.5 x 22 in.
Frequently Asked Questions
All resin-based 3D printing technologies produce waste resin. In its liquid form, resin is classified as a hazardous material. However, during the 3D printing process, resins are transformed from a liquid to a solid by being exposed to UV light.
Here is an overview of how waste resin is produced in the three most prolific resin 3D printing technologies:
PolyJet 3D Printing Technology
PolyJet 3D printers work by inkjet printing tiny droplets of resin one layer at a time on a build platform. The UV lights attached to the print head simultaneously cure the resin, forming a single, fully cured cross-section of the parts on the build platform. Once a cross-section is completed the build platform is lowered in the Z-direction, and the process is repeated for the next layer until the part is completed.
PolyJet waste resin is generated in the following three ways:
- Interval Cleaning: At pre-determined intervals during the print process, the print head travels to the side of the build platform and automatically jets small amounts of resin through the print head nozzles into a waste reservoir. This process clears the nozzles and, in effect, cleans the print heads. Although a very small amount of material gets wasted in each interval, this process continues, and waste accumulates over time.
- Material Changeover: When an operator loads the printer with a different resin there is a purge cycle to clear the printer of the previously used resin. For example, when changing from VeroBlack to VeroWhite, the VeroBlack that is residing in the printer’s heads and hoses are purged into the waste container.
- Expiration: PolyJet materials have a shelf life of 12 to 14 months and will expire if left unused. Each container has an RFID tag with an expiration date. This prevents damage to the printer since the material will coagulate and clog up the print heads.
SL (Stereolithography) 3D Printing Technology
SL 3D printers work by beaming a UV laser onto a vat filled with UV light-sensitive resin. When the laser hits the resin, it cures it from liquid to solid. After parts are printed and removed from the vat, the user must pour the additional resin into the vat to “top-it-off.” Typical vat volumes are anywhere from .2 Liters (Formlabs Form 2) to 400+ Liters (3D Systems ProX 800 and Stratasys Neo 800).
SL waste resin is generated in the following ways:
- Post Processing: When cleaning SL parts, the parts are bathed in IPA (Isopropanol), which removes any excess uncured waste resin. Over time, the IPA becomes semisaturated with uncured waste resin and must be disposed of.
- Contamination: SL systems utilize an open vat configuration. If the vat getscontaminated with foreign debris or partially cured remnants from previous print runs, then it needs to be replaced.
- Expiration: SL resins have a shelf life of 18 to 24 months. Upon expiration, the material must be disposed of properly.
DLP (Digital Light Projection) Technology
DLP 3D printers work by using a UV light projector and flashing an image onto a vat (build tray) filled with resin. When the UV light image is projected onto the resin, the resin is partially cured from a liquid to a solid. After parts are printed and removed from the vat, the user must pour the additional resin into the vat to “top-it-off.” Typical vat volumes are small which enables the user
to easily change build trays.
DLP resin is generated in the following ways:
- Post Processing: When cleaning DLP parts, the parts are bathed in IPA (Isopropanol), which removes any excess uncured waste resin. Over time, the IPA becomes semi-saturated with uncured waste resin and must be disposed of.
- Expiration: DLP resins are more unstable than SL resins and typically have shorter shelf lives. Some of the two-part resins, such as the EPX 82 from Carbon 3D, once mixed, only last for 24 hours and must be disposed of. Some Carbon 3D customers report disposing of as much as 1 gallon per month of uncured DLP resin.
All resin-based 3D printing technologies produce waste resin. Although waste resin is considered hazardous in its liquid form, there are several options available to deal with waste resin. This paper touches on most of the issues related to this subject and points out that users may be subject to a combination of federal, state, and local regulations.
Option 1: Hazardous Waste Disposal Service
The first option is to hire a Hazardous Waste Disposal Service (HWDS) to pick up your waste resin. Many different companies offer this service. Please note, providers in your area may or may not process waste locally.
US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Registration
HWDS companies require your registration with the EPA, which requires a one-page application and a $40 fee. This will classify your company as a generator of hazardous waste, and you will be required to file a biannual report and renew your registration annually.
Depending on how much waste resin is generated, users will be assigned a classification, such as Small Quantity Generator (SQG) >2,200 lbs. per year or Large Quantity Generator (LQG) <2,200 lbs. per year. Among other regulations, classification determines the length of time a waste generator is allowed to store hazardous waste onsite; an SQG has up to 180 days and an LQG has up to 90 days.
To manage and ship hazardous waste, most HWDS companies require customers to complete Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) training. As the waste generator, the user maintains all liability for the storage drum and is required to complete a Uniform Hazardous Waste Manifest Form prior to sealing, labeling, and shipment. Additional documentation may be required based on a user’s location.
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
You will be asked to provide the MSDS of your resin to the HWDS. Their staff will review the MSDS and upon receipt of the waste resin, they will perform lab testing prior to disposal.
Type of Disposal
HWDS companies offer two types of waste resin disposal 1) Landfill and 2) Waste to Energy Incineration. The latter being the more expensive option. Depending on your area and HWDS, typical costs for disposal of a 55 gallon drum of waste resin could be $125 to $175 for landfill and $200 to $300 for incineration.
Other Considerations
Subject to location, HWDS companies are, by law, limited to storing hazardous waste at holding sites for a maximum of 10 days. In the current environment, many HWDS companies are backed up due to the overproduction of hand sanitizers, which, due to
high alcohol content and flammability, must be sent off to incinerators. For example, users located in California should consider how the timing of disposal may be impacted by the additional regulations for storage and shipment placed on HWDS companies, which must dispose of hazardous waste at sites located out of state. Also, storing location, floor space and general liability of hazardous waste storage should be considered.
Amount of Waste Resin
The amount of waste resin produced will determine the cost of your service. Typically, waste resin is stored in a 55 gallon drum ($75 to $300). Drums and storage containers can either be sourced through the HWDS or from an industrial equipment supplier, such as Grainger.
Other Fees
With each pickup, or “Milk Run,” there are several fees to be aware of, including: driver fees ($85 to $100 per hour, typically 2 hour minimum), manifest fees ($25 to $50), and environmental services charges (typically 15% surcharge).
Option 2: California Lunch Tray Method
The second option is a DYI process, in which users pour waste resin onto a lunch tray or metal baking pan and let it cure outside under sunlight. The UV light from the sun will slowly cure the resin. The resin must be poured periodically in thin layers to maximize the surface area of sun exposure. The user must periodically stir the waste resin to ensure that underlayers of uncured resin are exposed to UV light.
Face masks and gloves are required for protection from the caustic process. Processing times can vary, depending on temperature and weather. When cured, the solid resin can be disposed of as common household waste.
Option 3: Waste Resin Axial 3D Printing (WRAP) Technology
A third option is to use Waste Resin Axial 3D Printing (WRAP) Technology to cure waste resin. WRAP technology enables safe curing through a patented process in which a user pours the resin into the system’s vat. The resin is slowly dispensed in drips onto a disposable paper-based cylinder located in a chamber with high-powered UV lights. As the resin drips and the cylinder rotates, the resin is instantly cured. The process continues until the full volume of waste resin in the vat is exhausted, leaving a cylinder of cardboard and solid cured plastic stock. When cured, the solid resin can be disposed of as common household waste or repurposed for various applications, including low-cost media for CNC machining.
ADDITIONAL 3D Printing RESOURCES
AWARD-WINNING TECHNICAL SUPPORT
GoEngineer’s extensive technical knowledge can assist with your additive manufacturing needs. Our Award winning team is ready to help. Reach out and see why GoEngineer is the #1 reseller of SOLIDWORKS and Stratasys systems in the world!
3D Printing Courses
Learn to utilize all features and tools of Stratasys commercial 3D printers with GoEngineer additive manufacturing on-boarding training and 3D printing courses. Take advantage of our 3D printing team of experts to help launch all your 3D printing capabilities.
3D PrintING SERVICES
No matter the size, quantity, or complexity of part(s) needed, GoEngineer can help you! Take advantage of our 3D Printing Services to help your organization produce the best parts and prototypes available on the market.
Additional Resources
Take Advantage of GoEngineer’s Extensive Knowledge Base and Resources

Find a Solution
Our robust Knowledge Base contains over 12,000 resources to help answer your product design questions. From basic CAD questions to in-depth guides and tutorials, find your solution here. Find a Solution

PROFESSIONAL TRAINING
Improve your skills with professional training and certifications in SOLIDWORKS, CAM, 3D Printing, and 3D Scanning offered four ways: self-paced, online, on-site, or in-classroom. Certified Training Courses

BLOG
#1 Technical Resource Worldwide - Right at your fingertips. Search or browse through hundreds of SOLIDWORKS tips & tricks, additive manufacturing product developments, announcements, how-to guides, and tutorials. Blog

YouTube Channel
Our YouTube channel hosts hundreds of educational tutorials, product demonstrations, recorded webinars, and best practices for all of our products and services. GoEngineer's YouTube Channel

ONLINE STORE
Order 3D printing materials and consumables, enroll in SOLIDWORKS training classes, and buy official GoEngineer gear directly from our online store. Online Store

WEBINARS
Our engineering webinars are hosted by some of the top experts in the industry. They are always recorded, always free, and always offer a live Q&A. WEBINARS

3D Printing Services
Need to 3D print a part? Our Additive Manufacturing experts will 3D print your part and deliver it to you using the latest technology on one of our professional FDM, PolyJet and SL 3D printers. 3D Printing Services