Guide to VDI: Types, Advantages, Considerations, and More
In 2020, when the demand for remote learning and online SOLIDWORKS training increased, GoEngineer transitioned from physical PCs and classrooms to virtual workstations using a VDI. With this solution, we were able to efficiently maintain and support training machines for remote learning environments.
Note: GoEngineer does not provide implementation services, advice, or diagnostics support for VDI.
What is VDI and How Does it Work?
VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) is a system that uses virtual machines to provide and manage virtual desktops. VDI hosts desktop environments on a centralized server and deploys them to the end user on request.
In VDI, a hypervisor segments servers into virtual machines that, in turn, host virtual desktops that users can access remotely from any device anywhere. Users connect to their desktop instance through a connection broker, a software-based gateway that acts as an intermediary between the user and the server.
Persistent VDI vs Nonpersistent VDI
VDI can be either persistent or nonpersistent. Each type offers unique benefits:
With persistent VDI, a user connects to the same desktop each time and can personalize the desktop since changes are saved even after the connection is reset. In other words, desktops in a persistent VDI environment act exactly like personal, physical desktops.
In contrast, with nonpersistent VDI, users connect to generic desktops and changes are not saved. This is usually simpler and more affordable since there isn't a need to maintain customized desktops between sessions. Nonpersistent VDI is often used in organizations with many task workers or employees who perform a limited set of repetitive tasks and don’t require a customized desktop.
Here is the VDI network layout for all the Horizon product suites within the VMWare Infrastructure.
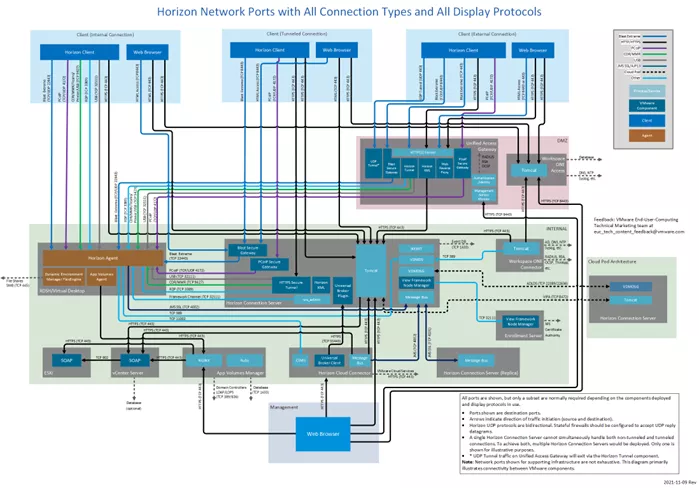
Click here for a closer look at this image and to access additional information about Network Ports in VMware Horizon.
What's the Difference Between VDI and Virtual Machines (VMs)?
Virtual machines (VMs) are the technology that powers VDI. VMs are software “machines” created by partitioning a physical server into multiple virtual servers through the use of a hypervisor. (This process is also known as server virtualization.) Virtual machines can be used for a number of applications, one of which is running a virtual desktop in a VDI environment.
We chose VMWare as the VDI infrastructure because it was the most reliable hypervisor platform, it met the needs of the project, and we already had VMWare experience.
A big advantage of utilizing the VDI is the ability to create instant clones and build and/or update multiple training machines within minutes.
With VDI, we can utilize the graphics passthrough, which allows us to configure GPU usage. This allows us to tap into more VDI computer power by using Virtual Dedicated Graphics Acceleration (vDGA) and/or NVIDIA GRID Virtual GPU (vGPU). The VMware Video Card will not process 3D operations and thus ensures the passthrough graphics device will receive the 3D operations.
VDI – What Does it Look Like?
The appearance of the VDI does not look significantly different than our own desktop display.
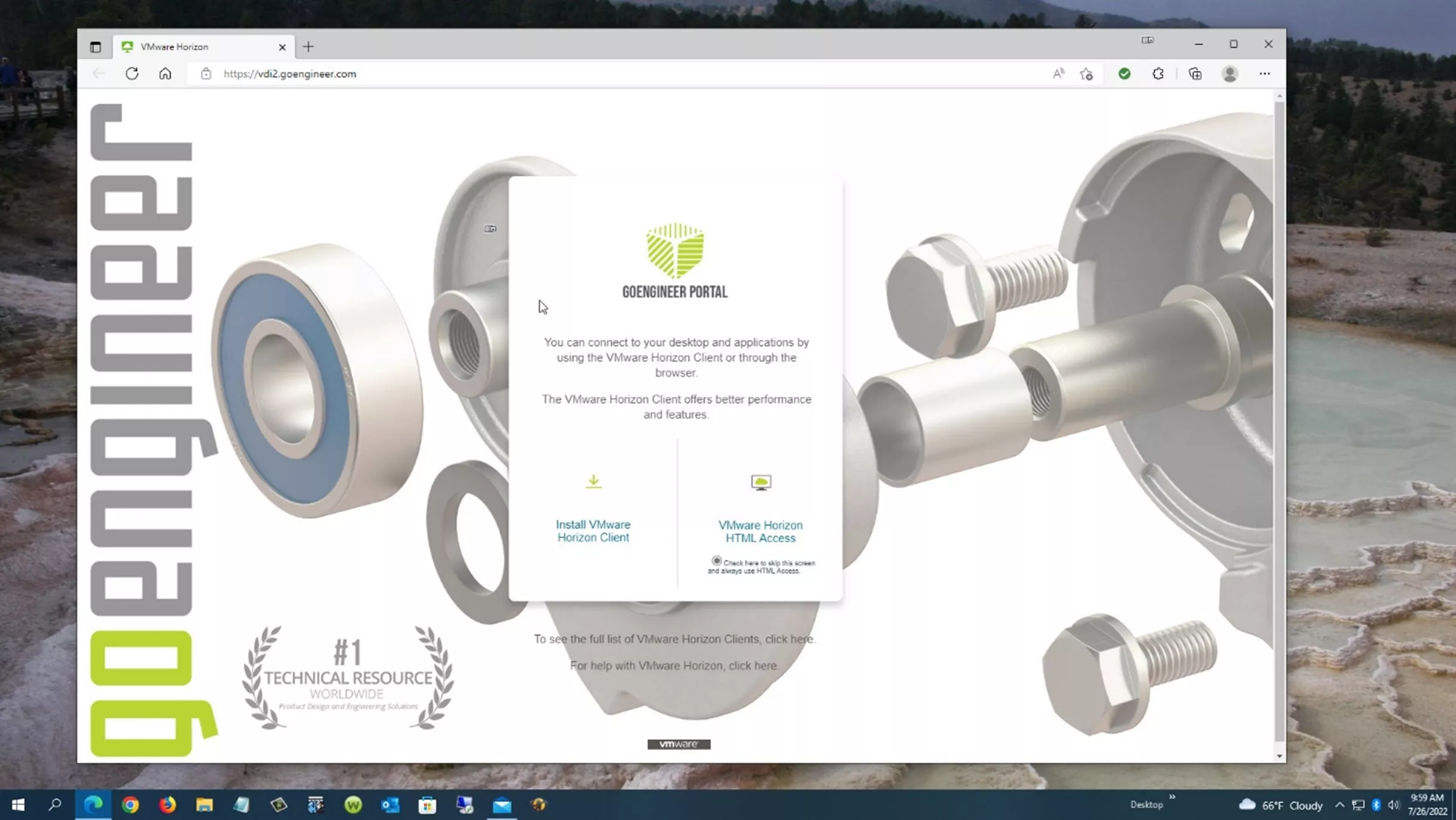
I logged in using the HTML.
Then SOLIDWORKS 2022.
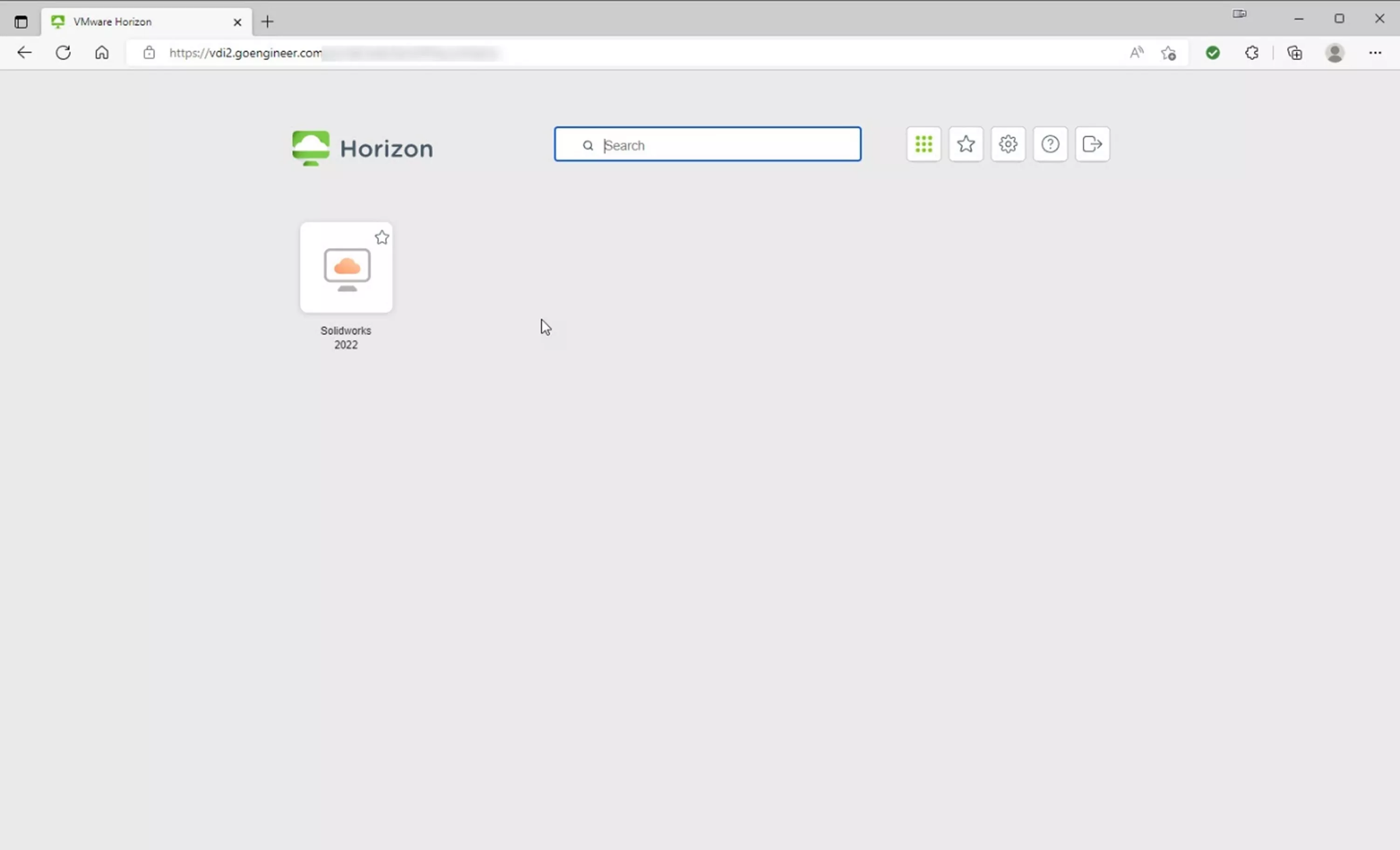
The horizon control panel.
Pros and Cons
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using VDI?
Pros
- Performance
- Unified experience
- Better control
- Remote users
- Remote troubleshooting
- Centralized Management
- BYOD – (Bring Your Own Device)
The ability to access VDI from any device simplifies how we can utilize our VDI, as no specialized equipment is needed. BYOD VDI is an ideal solution for environments that allow or require employees to use their own devices. Since processing is done on a centralized server, VDI allows the use a wide range of devices. It also offers better security since data lives on the server and is not retained on the end client device.
VDI is centralized in one location, so it's cheaper to maintain the independent computer and it's easier for IT to perform the troubleshooting.
Performance and unified experiences are also better as the VDI uses the server resources, CPU, and GPU for each virtual desktop. Since these desktops are cloned, they are identical.
Cons
- Upfront cost
- IT Know-how
- Outages/Failures
- Occasional user issues
Initial setup cost is a bit of a drawback and not all IT professionals may be familiar with setup, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Additionally, if the server has a power outage, all users will lose access simultaneously. The user's hardware and/or bandwidth or internet connection issues can also negatively impact the accessibility and use of the VDI.
VDI Guidelines (Considerations)
Before building your VDI, you should consider how many users you will have and may need to add in the future. How will they be using the VDI? What are their software graphics and memory needs? Answering these questions will help us build our server. Also, consider having backups or multiple servers as well.
Here is a list of the considerations we looked at when building our VDI.
- Guidelines for VDI (considerations)
- Usage – how many users, what will they be doing, graphic dependent
- Number of users
- Graphics needs
- Memory needs
- Number of Servers
- It can be more cost-effective to build multiple servers rather than overload a single server with enough memory and computing power to run 100s of users.
- Processor
- Cores per user
- 3.3Ghz or higher for SOLIDWORKS
- Memory
- Total users' memory needs will define the memory requirements
- Include additional memory for VMWare Components to run.
- Graphics
- Total Graphics needs will define the card needed and the number of cards (Users * Graphics Memory Per User) = Total Graphics Needed.
- Storage
- Fast SSD Storage
- Internet Speed
- Bandwidth - Plan for 1.5Mbps/User
- Supported Hardware
- vSphere ESXi Certified
- Virtual Dedicated Graphics compatible
Costs to implement and maintain
For an idea of the cost and maintenance of the VDI, here are some approximations.
- For 48 Users, 3 Year Commitment/Investment
- Server - $30,000 + 3 Year Warranty
- Vmware Horizon Ent - ~$200/User/Year (Includes licenses for ESXI, VCenter, Horizon)
- NVIDIA - ~$250/User/Year
- Power
- IT Support
The video below demonstrates how our SOLIDWORKS students can access our VDI.
VDI Web links
Here are some additional resources that you might find helpful and informative.
Older NVIDIA Grid FAQ
Creating Golden Image
NVIDIA VGPU Blog
NVIDIA Free Trial
VMware vGPU compatibility
NVIDIA Horizon Deployment Guide (old, 2018)
- https://images.nvidia.com/content/pdf/vgpu/guides/vgpu-deployment-guide-horizon-on-vsphere-final.pdf
NVIDIA vGPU resources (Datasheets, whitepapers)
Horizon Licensing, Minimum License - Horizon Standard
Dell VDI Design Guide - VMware Horizon on VxRail and vSAN Ready Nodes
Related Articles
Free SOLIDWORKS Training for Veterans
Obtaining and Using SOLIDWORKS Certification Exam Vouchers
Learn SOLIDWORKS Online: Virtual Classroom vs. Self-Paced Training

About Matthew Kusz
Matthew Kusz is a Senior Technical Support Engineer at GoEngineer. When Matthew isn’t assisting customers with their engineering challenges, he spends his free time repairing antique watches/clocks, designing furniture, tending his aquariums and learning about bee keeping.
Get our wide array of technical resources delivered right to your inbox.
Unsubscribe at any time.